This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Mystic Help
Lookup Manager Concept Overview
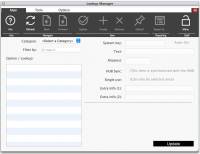 The [Lookup Manager] is a dialog intended to perform two specific functions, and is accessible only to suitably authorised staff users:
The [Lookup Manager] is a dialog intended to perform two specific functions, and is accessible only to suitably authorised staff users:
- Manage system level, application wide configuration settings which affect all dialogs and all users
- Manage the various drop-down lists and foundation information which is used within other manager dialogs around the application
The [Lookup Manager] is laid out in a very similar way to most Mystic managerial dialogs. A list on the left hand side of the dialog allows you to choose a value that you wish to edit, as well as Category and Filtering options to reduce the number of values being displayed at any one time (the Keyword Category for example, may contain tens of thousands of entries).
When selected, the details of an entry appears on the right-hand side of the dialog. Depending upon what type of Category is being edited, fewer fields may be made available or entirely new editing sections that are specialised for that Category may appear.
In all other respects, use of the [Lookup Manager] follows the standard pattern:
- Select a Category and Entry to edit
- Edit the details
- Update the details
Note however, that because the [Lookup Manager] is responsible for managing foundation data from around the Mystic database:
- Many values that can be found in the Lookup Manager may be created and managed by other functional areas (e.g. creating new Keywords while cataloguing in the Catalogue Item Manager) without the need to use this dialog
- A number of additional specialised functions and tools are provided (see links below).
Categories
Mystic divides the various foundation data into Categories, each of which is of a specific type (or usage). The Category Types are:
- Item Indexing
- Item Popups
- Item Qualifiers
- Reader Indexing
- Reader Popups
- Reader Qualifiers
- System
If you do not see a particular category in the Lookup Manager which you wish to edit, it may simply be that their display is turned off. In order to make it visible, select the [Options] toolbar tab and toggle on the toolbar icons in the [Reader Categories], [Item Categories] or [System] toolbar groups as required.
The Indexing Category Types represent foundation data which may appear in connection with a particular type of record (items, readers etc) any of which may be used multiple times within the same record. Such foundation data may therefore include Keywords and Contributors (i.e. Authors) as several different values of each type may be attached to the record.
The Popup Category Types represent foundation data which would normally appear only once within a particular type of record and therefore typically is used to populate drop-down lists where only a single selection can be made. Such foundation data may therefore include Publishers, Series Titles, Student Classes etc.
The Qualifier Category Types contain additional information which is combined with the above to add particular meaning to the specific use of that value in single cases. In the case of Contributors for example, individuals may be attached to items as Authors, Illustrators, Editors, Actors, Directors etc. and may be attached multiple times to the same record, each with a different Qualifier.
The System Category Types contain foundation data which is used to configure Mystic, or otherwise inform Mystic how to operate.
Standard Categories
The Lookup Manager has a number of core categories of information which are available in all versions of Mystic, as well as a number of custom categories which may have been created by Esferico on the behalf of Mystic users or by suitably authorised Mystic users with access to the Category tools.
Standard categories include:
Item Indexes
- Audience - item Audiences define what type of audience an item is intended for. In most educational environments containing a single age group, the default Suitable For All audience is typically used for all items. The audience set for any item is used in conjunction with the Reader Audience setting to determine whether the item can be borrowed by that individual.
- Categories - Item Categories (not to be confused with Catalogue/Category Types, see below) represent a foundation data pick-list of standard categorisations within a classification type. The Item Categories category therefore includes all of the possible values in something like the Dewey classification system. Unless a small-range classification is in use, they are typically not used by most library environments due to the excessive number of possible values involved.
- Contributors - The Contributors category contain all authors, illustrators etc. who have contributed to the creation of items stored in the catalogue. Often, staff simply refer to this data field as 'authors'. In most cases, the Contributor values are created and managed directly from the Catalogue Items Manager.
- Keywords - The Keywords category contains all keywords that have been attached to catalogue items in order to allow indexing, searching and filtering by both readers and staff users. By their very nature, the Keywords category can grow to significant numbers. Again, the addition of keywords is usually performed within the Catalogue Items Manager as a part of conventional cataloging.
- Languages - The Languages category is used to provide a list of languages which are used / supported by a particular item. Unless the library contains multi-lingual items, this category is rarely used by most library environments. A second use of this category however, is to provide a list of languages and language variants for use in the Mystic application language editor, which determines what words and phrases are displayed on buttons, menus, message etc.
- Provenance - The Provenance category lists the types of sources where the item or item information originated. The most common provenances in use as the names of vendors (who provide importable data about a purchased book) and 'Manual Data Entry'.
- Publishers - The Publisher category contains the list of publishers who have printed and produced a book, or the production company in the case of videos, movies etc. Typically, new publishers are created during the cataloging process within the Catalogue Item Manager.
- Reading Levels - The Reading Levels category is not used by the majority of educational environments, though many SLS (School Library Services) promote correct reading level projects.
- Subjects - The Subjects Category is an additional indexing method, similar in nature to Keywords but usually restricted to a single, generalisation of the purpose of the item. While an item may have many keywords in place regarding the various topics within a book on medicine for example, the attached Subject may simply be 'Medical'.
- Vendor - The Vendor category allows the library to record where the item was purchased from.
Item Popups
- Category (Catalogue) Types
- HID Formats (i.e. Barcode formatting options)
- Keyword Packages
- Media
- Series
- Status
- Storage Location
- Title prefixes
Item Qualifiers
- Contributor Qualifiers
Reader Indexes
- Audience
- Gender
- Protected Characteristics
Reader Popups
- Age Range - Age groupings into which Readers can be placed to restrict access to various types of item in the catalogue. At time of writing, the Age Range group is only used for library information and does not directly influence circulations rules (instead, see Audience).
- Circulation Profile - the Circulations Profile is the core setting which determines how many items are permitted to be borrowed by a reader, as well as for how long. Many Mystic users define a single Profile for conventional readers (set to be the default), and a single Profile for staff.
- Groups (e.g. Classes) - the Groups category lists the various groups into which readers can be organised. In the case of Education users, this category equates directly with school classes.
- HID Formats (i.e. Barcode formatting options) - HID Formats (Human readable IDs) define the format of how barcodes should be built or interpreted when scanned. In most cases, Mystic users define a single standard format and set it as the default.
- Locations - Reader locations should not be confused with Groups. Reader locations are used to define a physical location of a reader. Under normal circumstances, this category is used with a single default value or even not at all. Multiple reader locations are typically only defined by specialised library environments, or Mystic users with multiple physical sites (e.g. an Academy user with multiple schools, utilising a single library catalogue).
- OPAC Permissions - OPAC permissions define which features of the OPAC are permitted to an individual user when they login.
- Salutations - Salutations define the various prefixes that can be used for readers and include standard values such as Mr., Mrs., Miss, Dr., Prof. etc. They are rarely used in most educational environments, but see more use in industrial and commercial libraries.
Reader Qualifiers
- There are no Reader Qualifier categories at this time.
System
- Accessibility Options
- Audit Log Events
- Booking Destinations
- Closure Days
- Installed Lookup Packages
- Package Events
- Package Names
- Protected Characteristic Types
- System HUB
- System Information
- System Licenses
- User Group Names
- User Group Permissions
- User Permissions
